Java @Contended 避免缓存行伪共享
Java juc About 5,520 words相关名词
CPU缓存、缓存行、伪共享。
CPU 缓存
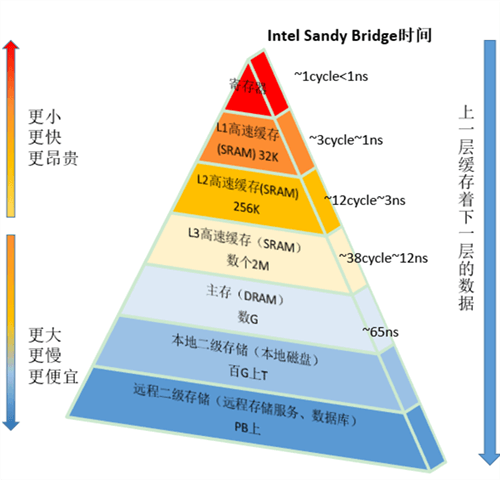
缓存行 Cache Line
CPU读取内存数据时并非一次只读一个字节,而是会读一段字节长度(不同CPU架构读取的长度不一样,常见的大小是64字节)的连续的内存块,这些块我们称之为缓存行。
但缓存行在高并发场景下会有性能问题:伪共享。
伪共享 False Sharing
当一个CPU要修改某共享变量A时会先锁定自己缓存里A所在的缓存行,并且把其他CPU缓存上相关的缓存行设置为无效。但如果被锁定或失效的缓存行里,还存储了其他不相干的变量B,其他线程此时就访问不了B,或者由于缓存行失效需要重新从内存中读取加载到缓存里,这就造成了开销。所以让共享变量A单独使用一个缓存行就不会影响到其他线程的访问。
适用场景
主要适用于频繁写的共享数据上。如果不是频繁写的数据,那么CPU缓存行被锁的几率就不多,所以没必要使用了,否则不仅占空间还会浪费CPU访问操作数据的时间。
测试代码
public class FalseSharing implements Runnable {
public final static int NUM_THREADS = 4; // change
public final static long ITERATIONS = 500L * 1000L * 1000L;
private final int arrayIndex;
// private static VolatileLong[] longs = new VolatileLong[NUM_THREADS];
// static {
// for (int i = 0; i < longs.length; i++) {
// longs[i] = new VolatileLong();
// }
// }
// private static VolatileLong2[] longs = new VolatileLong2[NUM_THREADS];
// static {
// for (int i = 0; i < longs.length; i++) {
// longs[i] = new VolatileLong2();
// }
// }
private static VolatileLong3[] longs = new VolatileLong3[NUM_THREADS];
static {
for (int i = 0; i < longs.length; i++) {
longs[i] = new VolatileLong3();
}
}
public FalseSharing(final int arrayIndex) {
this.arrayIndex = arrayIndex;
}
public static void main(final String[] args) throws Exception {
long start = System.nanoTime();
runTest();
System.out.println("duration = " + (System.nanoTime() - start));
}
private static void runTest() throws InterruptedException {
Thread[] threads = new Thread[NUM_THREADS];
for (int i = 0; i < threads.length; i++) {
threads[i] = new Thread(new FalseSharing(i));
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.start();
}
for (Thread t : threads) {
t.join();
}
}
public void run() {
long i = ITERATIONS + 1;
while (0 != --i) {
longs[arrayIndex].value = i;
}
}
// 12494250839
public final static class VolatileLong {
public volatile long value = 0L;
}
// 7647475236
// long padding避免false sharing
// 按理说jdk7以后long padding应该被优化掉了,但是从测试结果看padding仍然起作用
public final static class VolatileLong2 {
volatile long p0, p1, p2, p3, p4, p5, p6;
public volatile long value = 0L;
volatile long q0, q1, q2, q3, q4, q5, q6;
}
// 7729325748
// jdk8新特性,Contended注解避免false sharing
// Restricted on user classpath
// Unlock: -XX:-RestrictContended
@sun.misc.Contended
public final static class VolatileLong3 {
public volatile long value = 0L;
}
}@Contended
/**
* <p>An annotation expressing that objects and/or their fields are
* expected to encounter memory contention, generally in the form of
* "false sharing". This annotation serves as a hint that such objects
* and fields should reside in locations isolated from those of other
* objects or fields. Susceptibility to memory contention is a
* property of the intended usages of objects and fields, not their
* types or qualifiers. The effects of this annotation will nearly
* always add significant space overhead to objects. The use of
* {@code @Contended} is warranted only when the performance impact of
* this time/space tradeoff is intrinsically worthwhile; for example,
* in concurrent contexts in which each instance of the annotated
* class is often accessed by a different thread.
*
* <p>A {@code @Contended} field annotation may optionally include a
* <i>contention group</i> tag. A contention group defines a set of one
* or more fields that collectively must be isolated from all other
* contention groups. The fields in the same contention group may not be
* pairwise isolated. With no contention group tag (or with the default
* empty tag: "") each {@code @Contended} field resides in its own
* <i>distinct</i> and <i>anonymous</i> contention group.
*
* <p>When the annotation is used at the class level, the effect is
* equivalent to grouping all the declared fields not already having the
* {@code @Contended} annotation into the same anonymous group.
* With the class level annotation, implementations may choose different
* isolation techniques, such as isolating the entire object, rather than
* isolating distinct fields. A contention group tag has no meaning
* in a class level {@code @Contended} annotation, and is ignored.
*
* <p>The class level {@code @Contended} annotation is not inherited and has
* no effect on the fields declared in any sub-classes. The effects of all
* {@code @Contended} annotations, however, remain in force for all
* subclass instances, providing isolation of all the defined contention
* groups. Contention group tags are not inherited, and the same tag used
* in a superclass and subclass, represent distinct contention groups.
*
* @since 1.8
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target({ElementType.FIELD, ElementType.TYPE})
public @interface Contended {
/**
* The (optional) contention group tag.
* This tag is only meaningful for field level annotations.
*
* @return contention group tag.
*/
String value() default "";
}JEP 规范
指定字段减少缓存竞争。
Views: 3,385 · Posted: 2021-09-27
——— Thanks for Reading ———
Give me a Star, Thanks:)
https://github.com/fendoudebb/LiteNote扫描下方二维码关注公众号和小程序↓↓↓

Loading...